1. 背景
ffmpeg编解码涉及很多源文件,核心数据是AVFrame,本文将从视频解码入手,尝试弄清楚代码如何围绕着AVFrame完成初始化、编码或解码、使用以及生命周期,就可以梳理出大致脉络。
2. 解码
下面这张图画出大致解码过程中的几个关键源文件及关系,BTW,画图时找到一个超赞的国风调色板:
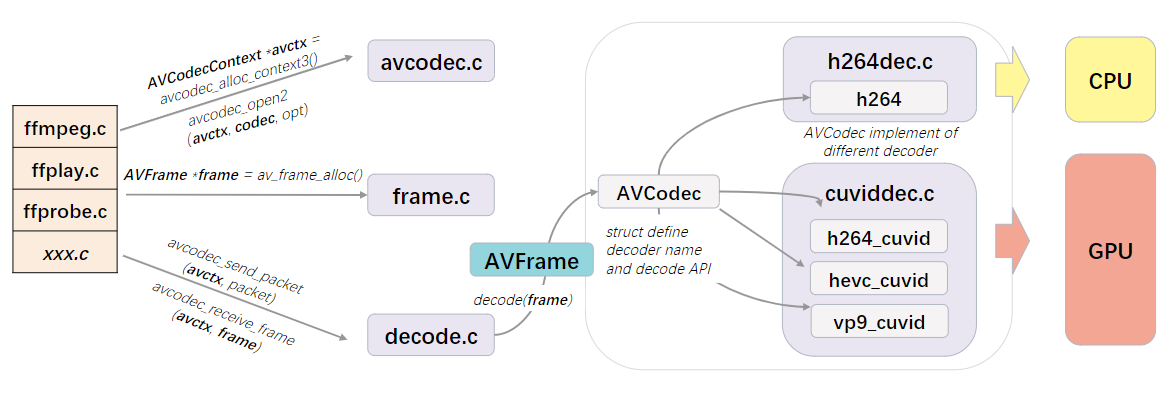
2.1. 初始化
首先ffmpeg.c/ffplay.c/ffprobe.c或是你基于ffmpeg库开发的相关xxx.c,都要先调用avcodec_alloc_context3拿到一个AVCodecContext *的返回值avctx,顾名思义是一个音视频编解码器的上下文。接下来为将要解码的数据流选择解码器,也就是一个AVCodec实例codec。涉及到的API有:
- allcodecs.c中的
avcodec_find_decoder() - allcodecs.c中的
avcodec_find_decoder_by_name()
随后通过av_dict_set()给codec准备参数,存储到AVDictionary类型的字典变量opt。最后调用avcodec_open2()把avctx、codec、opt捆绑到一起。
代码示例-裁剪自ffplay.c
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
avctx = avcodec_alloc_context3(NULL);
ret = avcodec_parameters_to_context(avctx, ic->streams[stream_index]->codecpar);
codec = avcodec_find_decoder(avctx->codec_id);
switch(avctx->codec_type){
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_AUDIO : is->last_audio_stream = stream_index; forced_codec_name = audio_codec_name; break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_SUBTITLE: is->last_subtitle_stream = stream_index; forced_codec_name = subtitle_codec_name; break;
case AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO : is->last_video_stream = stream_index; forced_codec_name = video_codec_name; break;
}
if (forced_codec_name)
codec = avcodec_find_decoder_by_name(forced_codec_name);
avctx->codec_id = codec->id;
opts = filter_codec_opts(codec_opts, avctx->codec_id, ic, ic->streams[stream_index], codec);
if (!av_dict_get(opts, "threads", NULL, 0))
av_dict_set(&opts, "threads", "auto", 0);
if ((ret = avcodec_open2(avctx, codec, &opts)) < 0) {
goto fail;
}
2.2. 解码
调用avcodec_send_packet()给avctx传入新的压缩包,同时调用avcodec_receive_frame()读取原始图像。
代码示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
static int decode(AVCodecContext *avctx, AVFrame *frame, int *got_frame, AVPacket *pkt)
{
int ret;
*got_frame = 0;
if (pkt) {
ret = avcodec_send_packet(avctx, pkt);
// In particular, we don't expect AVERROR(EAGAIN), because we read all
// decoded frames with avcodec_receive_frame() until done.
if (ret < 0 && ret != AVERROR_EOF)
return ret;
}
ret = avcodec_receive_frame(avctx, frame);
if (ret < 0 && ret != AVERROR(EAGAIN))
return ret;
if (ret >= 0)
*got_frame = 1;
return 0;
}
3. AVFrame
AVFrame是FFMPEG中解码后每帧图像或声音的基本单元,解码时先调用av_frame_alloc分配AVFrame实例,此时并没有为图像或声音数据分配空间,再通过avcodec_receive_frame传给解码器,解码器负责将解码后的图像或声音数据,关联到这个实例。
3.1. av_frame_alloc
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
AVFrame *av_frame_alloc(void)
{
AVFrame *frame = av_mallocz(sizeof(*frame));
if (!frame)
return NULL;
frame->extended_data = NULL;
get_frame_defaults(frame);
return frame;
}
3.2. h264dec窥探
h264dec.c中output_frame,通过frame.c中的av_frame_ref,把H264Context中的某个H264Picture的AVFrame,复制给应用这传入的AVFrame *src。
av_frame_ref发现src是null时,主动用av_frame_get_buffer()->get_video_buffer()来给src->data做初始化,真实的解码后图像空间放在src->buf中,然后src->data数组各通道被赋予src->buf空间的不同位置指针。此时通过av_frame_copy()->frame_copy_video()->av_image_copy()复制解码后图像到src->data。
- 应用src->buf:dst->buf[i] = av_buffer_ref(src->buf[i]);
- 复制src->data数组的图像空间地址到dst-data:memcpy(dst->data, src->data, sizeof(src->data));
3.3. 计算LineSize
libutils/imgutils.c提供av_image_fill_linesizes API根据给定图像类型、宽,计算对应linesize填写到传入的数组。
其中依赖libutils/pixdesc.c中全局struct数组:av_pix_fmt_descriptors,她描述了每种格式各通道数据的布局,比如:
- Planar平面模式,比如YU12(也叫I420),Y/U/V各在一个独立的连续存储空间。
- Semi-Planar半平面模式,比如NV12,Y和UV分别在独立的连续空间,而UV(CbCr)交错存储,而不是分为三个独立空间。
- Packeted打包模式,比如YUYV422各RGB,每个Y和UV相邻,三个通道都没有独立的连续空间。